Publication: A broadband acoustic stimulus is more likely than a pure tone to elicit a startle reflex and prepared movements
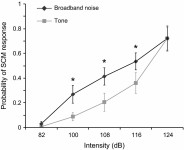
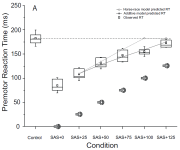
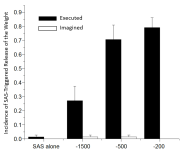
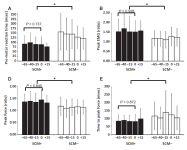
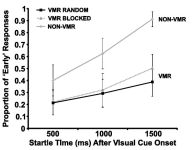
PDF In order to be able to confidently assert that any RT speeding following a startling acoustic stimulus (SAS) is the result of activation in subcortical areas related to the startle reflex, a reliable indication that a startle reflex actually occurred is required. While the eye-blink response is typically used…