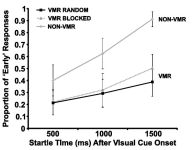
Publication: Self-controlled feedback is effective if it is based on the learner’s performance: a replication and extension of Chiviacowsky and Wulf (2005)
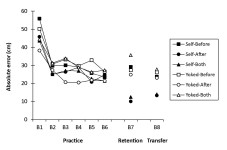
PDF This study looked at whether giving learners control over if (and when) they received feedback affected learning of a new task. The main finding is that learners who were able to choose to receive feedback after a trial performed better in retention and transfer. This suggests that the decision to…